Module 2
GRAMMAR
The Present Simple and the Present Continuous
*First of all we have to explain the difference between the simple present tense and the present continuous.
1.The Present Simple (affirmative , negative, and question).
Simple Present Uses
1: We use the present simple when something is generally or always true.
People need food.
It snows in winter here.
Two and two make four.
2: Similarly, we need to use this tense for a situation that we think is more or less permanent. (See the present continuous for temporary situations.)
Where do you live?
She works in a bank.
I don't like mushrooms.
3: The next use is for habits or things that we do regularly. We often use adverbs of frequency
(such as 'often', 'always' and 'sometimes') in this case, as well as expressions like 'every Sunday' or 'twice a month'. (See the present continuous for new, temporary or annoying habits).
Do you smoke?
I play tennis every Tuesday.
I don't travel very often.
4: We can also use the present simple for short actions that are happening now. The actions are so short that they are finished almost as soon as you've said the sentence. This is often used with sports commentary.
He takes the ball, he runs down the wing, and he scores!
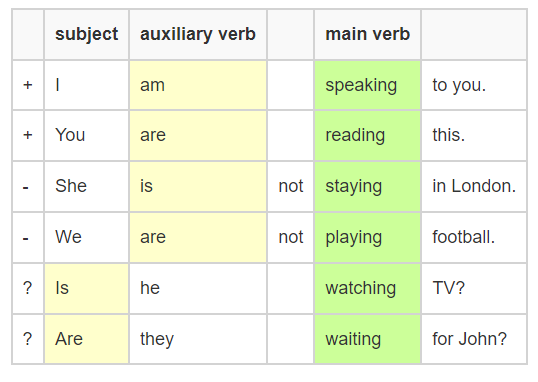
*Form:
Sub + v(base) + C. (For plural subject) they / you / we / I
They play out.
Sub + v(s/es) +C. (For singular subject) she / he / it
Salma goes to the school everyday.
**************************************************
The Present Simple (negative)
Form : Sub + don't/ doesn't + v (base)
Remmember: don't : for plural
doesn't : for singular
1.She does'nt eat fish.
*************************************
The Present Simple (interrogative)
*Form : Do / Does +sub + v(base) +C.
1.Do you like eating out?
2. Does Sam go watch horror movies?
2. We don't wear watches
********************************
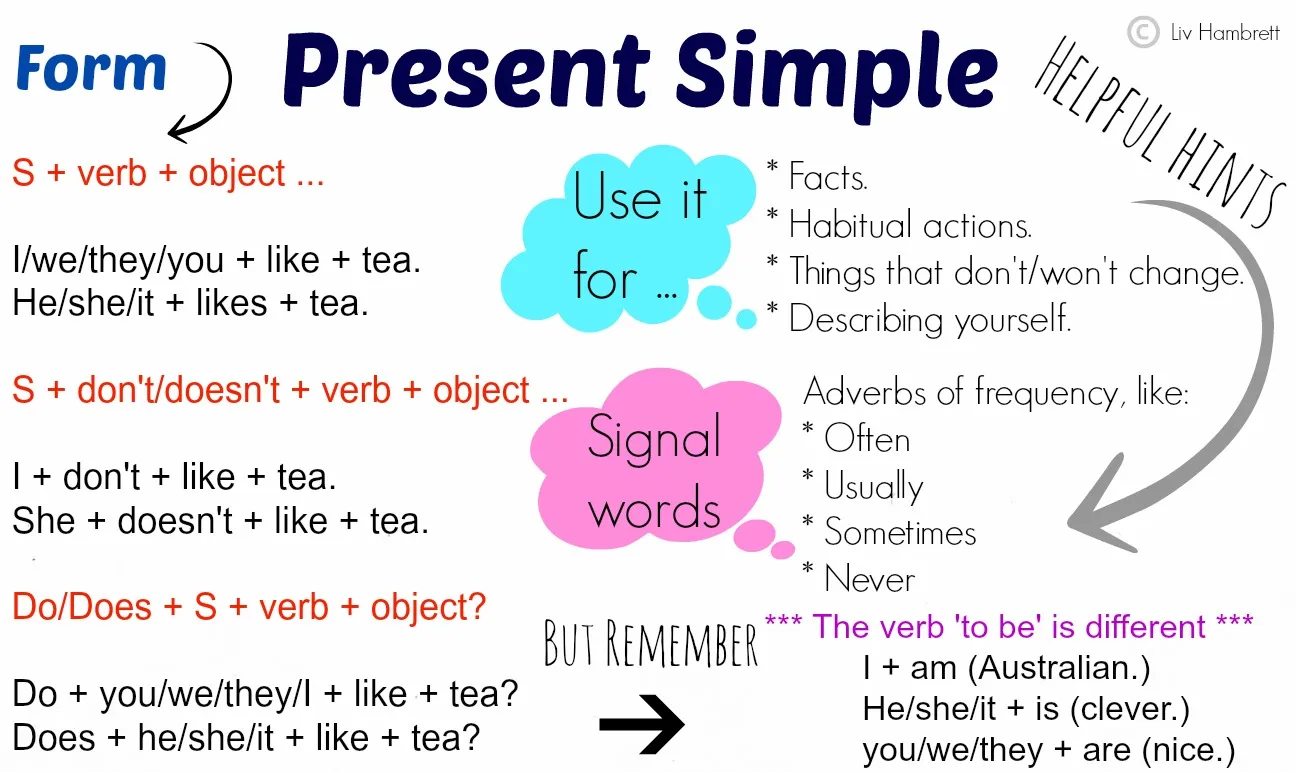
Remember: 'be' is different from the other verbs in this tense. Let's look at 'be' first:
| Positive | Positive Short Form |
| I am | I'm |
| you are | you're |
| he is | he's |
| she is | she's |
| it is | it's |
| we are | we're |
| they are | they're |
Next, here's the negative. It's very easy. You only add 'not'.
| Negative | Negative short form |
| I am not | I'm not |
| you are not | you aren't |
| he is not | he isn't |
| she is not | she isn't |
| it is not | it isn't |
| we are not | we aren't |
| they are not | they aren't |
| Yes / No Questions |
| am I ? |
| are you ? |
| is he ? |
| is she ? |
| is it ? |
| are we ? |
| are they ? |
*********************************************************************
2. Presint continuous:
also called Present Progressive)
We often use the Present Continuous tense in English. It is very different from the Present Simple tense, both in structure and in use.
We use the Present Continuous to talk about:
- action happening now
- action in the future
- ********************************************
- The main verb is invariable in present participle form: -ing
-
For negative sentences we insert not between the auxiliary verb and the main verb.
For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the auxiliary verb.
Look at these example sentences with the Present Continuous tense:
-
The structure of the Present Continuous tense is:
subject + auxiliary be + main verb conjugated in Present Simple am, are, is present participle (-ing) - *********************************************************
-
The auxiliary verb (be) is conjugated in the Present Simple: am, are, is
-
-
*More examples:
- We're eating at Joe's Cafe tonight. We've already booked the table..
- They can play tennis with you tomorrow. They're not working.
- When are you starting your new job?
- ****************************************************
| Basic rule: |
Just add -ing to the base verb: go : going walk: walking be: being |
||
|---|---|---|---|
vowels = a, e, i, o, u
| stop | → | stopping |
| run | → | running |
| begin | → | beginning |
| Exception | If the base verb ends in ie, change the ie to y: | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| lie | → | lying | |
| die | → | dying | |
| Exception | If the base verb ends in vowel + consonant + e, omit the e: | ||
| come | → | coming | |
| mistake | → | mistaking | |
***************************************************
GRAMMAR
SB page 13 / exercise 1:
1 Complete the interview with the words from the box.
| is / eating / am / cooking / making / are |
TV reporter: Why (1) _____ you travelling around Asia? Gary Rankin: Because I am (2) _____ a documentary about the local food. TV reporter: What is the chef (3) _____ for you? Gary Rankin: He (4) _____ making a traditional rice meal. The fi lm crew and I are (5) _____ great things during our trip! TV reporter: I (6) _____ looking forward to watching the TV series!
The answer :1. are; 2. making; 3. cooking; 4. is; 5. eating; 6. am
**************************************************
SB page 13 / exercise 2:
Read the sentences below. Then, put a tick next to the correct sentences and correct the ones that have wrong verb forms.
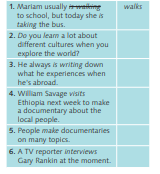
The answer: 1. is walking – walks
2. ✓
3. is writing – writes
4. visits – is visiting
5. ✓
6. interviews – is interviewing
**********************************************************************
SB page 13/ exercise 3:
3 Write three things about the lives of the Nyangatom.
Example.
Life is challinging for the Nyagantom.
Suggested answers
The Nyangatom live in Ethiopia.
They use herbs and plants for medicine.
They work hard to take care of their cattle.
******************************************************************************
SB page 13/ exercise 4:
4 Find these sentences in the text. Then, say which sentence, a or b, has the same meaning.
1. I'm staying with the Nyangatom tribe ...
a. I live with the Nyangatom tribe all the time.
b. I live with the Nyangatom tribe now.
2. I'm still planning many things.
a. I have more plans to make.
b. All the plans were made.
3. The people work very hard ...
a. The people are only working hard today.
b. The people always work hard.
The answer:1. b; 2. a; 3. b
******************************************************
SB page 14/ exrcise 5
Read the dialogue. Put the verbs in brackets into the Present Simple or the Present Continuous. Some verb forms might stay the same.
|
Adel: What (1) _______ (you / watch)? Badria: Oh! It’s a documentary about medical herbs. Adel: (2) _______ (there / be) any medical herbs in Jordan? Badria: Of course there are! I (3) _______ (try) to get information about them to see if they are nearby. Watch this interview with Dr Sabbagh. She’s a scientist. Dr Sabbagh: One of the most common medical herbs that we have in Jordan is “sage” [almaryamiya]. It is used as a herb in cooking, and (4) ____________ (have) a unique flavour. It has important health benefi ts and can make you (5) ____________ (feel) strong, too. Sage can be used to treat kidney and heart problems. A herb you almost certainly will have tried – “thyme” [zaatar] – is also used as medicine. It is good for keeping the mind alert. It wouldn’t hurt to eat some of this before an exam. Adel: What (6) _______ (we / wait) for? Badria and Adel: Let’s go and check! |
The answer: 1. are you watching 2. Are there 3. am trying 4. has 5. feel 6. are we waiting
*************************************************
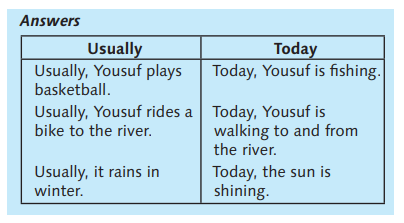
SB page 14 / exercise 7
Look at the picture of Yousuf. Write down what usually happens and then what is happening today, based on the table below.

*************************************************